
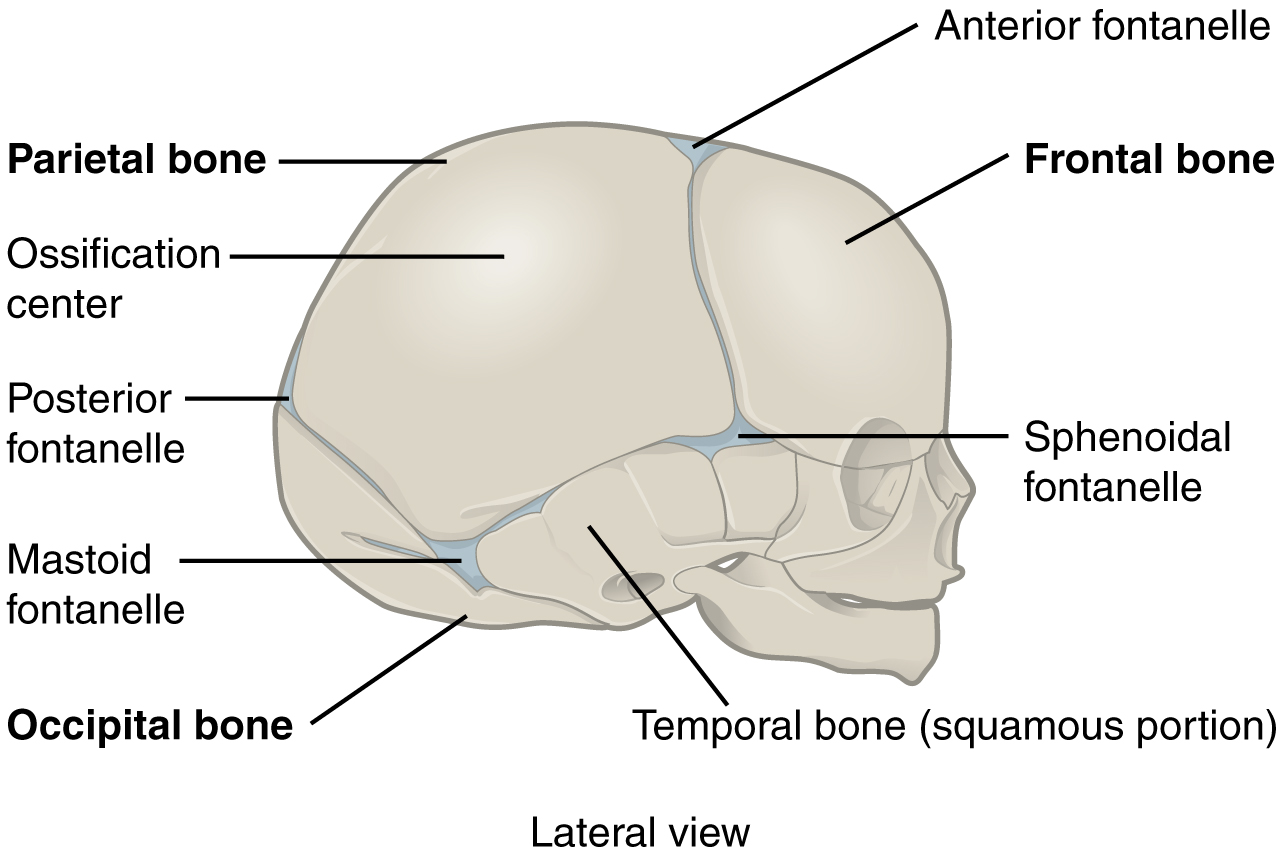
Each of the following facial bones are paired: the maxillae form the upper jaw and front of the hard palate the zygomatic bones form the cheeks the nasal bones form the bridge of the nose the lacrimal bones form part of the orbit, or eye socket the palatine bones form the rear of the hard palate and the inferior nasal conchae divide the nasal cavity. The 14 facial bones provide the structure of the face and form the openings through which food, water, and air enter the body. Shaped like a butterfly, the sphenoid bone forms the middle part of the cranial floor. The ethmoid bone forms part of the nasal cavity. The occipital bone forms the cranial rear and floor. Two temporal bones form the lower cranial sides. Two parietal bones form the sides of the cranial roof. By one-and-a-half years of age, the skull sutures have formed and the fontanels have disappeared. Fontanels allow the skull to be compressed slightly during birth and accommodate growth of the brain during early infancy. In newborns, the skull bones are not completely fused they are linked by fibrous membrane called fontanels. The mandible, or lower jaw, the only moveable skull bone, allows the mouth to open and close. The sutures lock the edges of the skull bones together, like pieces in a puzzle, to form a structure that is both rigid and strong. In adults, all but one of the skull bones are fused together by immovable joints called sutures. “Human skull side simplified (bones)” by LadyofHats Mariana Ruiz Villarreal – (Public Domain) via Wikimedia Commons “Gray194” by Henry Vandyke Carter – Henry Gray (1918) Anatomy of the Human Body (See “Book” section below): Gray’s Anatomy, Plate 194.The skull is made up of 22 bones: the cranium includes eight bones that surround and protect the brain and 14 bones that form the face. Skull: Skull has the cranial cavity and smaller sinuses.Ĭranium: Cranium makes the cranial cavity in which the brain is located. Skull: Skull protects the brain, provides a surface for muscle attachments and holds sensory organs for vision, hearing, speech and vision.Ĭranium: Cranium mainly protects the brain and provides surfaces for facial muscle attachments. Features of Skull and Cranium Number of bonesĬranium: Cranium consists of 8 bones called cranial bones.

Skull: Skull refers to the bones of the head collectively.Ĭranium: It is the bony portion of the skull that holds the brain.

What is the difference Skull and Cranium? Definition of Skull and Cranium The edge of each bone is joined with an adjacent bone edge through fibrous interlocking joints called ‘sutures’. The walls of cranial walls are composed of two plates. In addition, cranium provides a surface for the attachment of muscles that helps the movement of the head and supports the sense organs located in the head. The main role of the cranium is to protect the brain. Among these bones, parietal bones and the frontal bone are the largest. The eight bones include ethmoid, frontal, occipital, parietal (2), sphenoid, and temporal (2). The cranium is a subdivision of the skull that consists of 8 bones, which enclose the brain. Facial bones provide surfaces to muscle attachments and make passages to respiratory and digestive systems. Moreover, the skull is involved in speech, breathing, vision, and hearing. Most importantly, it provides protection for the most important organ of the nervous system the brain. The great architectural design of the skull reflects its many functions. The other several cavities found within the skull are called sinuses that accommodate the hearing and equilibrium structures. The main cavity of the skull that encloses the brain is called cranium cavity. The skull is located on the atlas of the vertebral column. The human skull is a complex structure consisting of 22 bones which mainly comprises cranial bones (8) and facial bones (14).
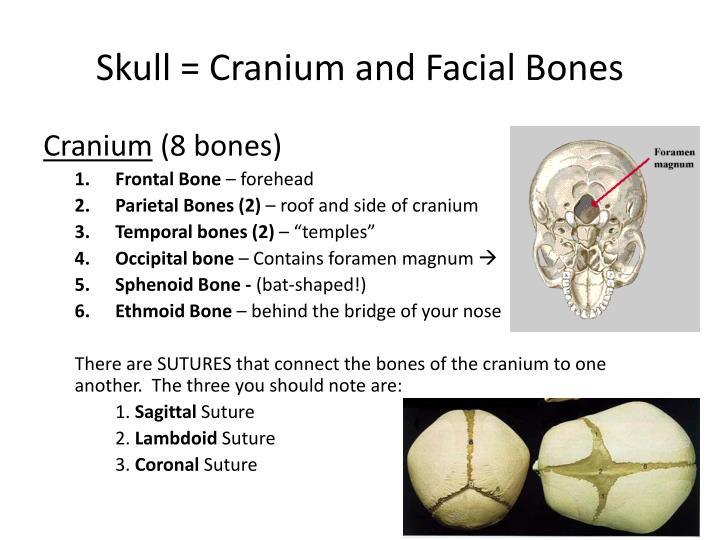
In this article, further differences between skull and cranium will be highlighted. The main difference between the skull and cranium is that skull is a complex structure containing 22 bones while cranium is a subdivision of the skull, containing only 8 bones. Skull and cranium are two important skeletal parts that protect the brain and supports other soft tissues located in the head, but a difference can be noted between them based on their structure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
